Are you wondering about the Cat5e maximum speed and how it fits into your home or office network? Cat5e, short for Category 5 enhanced, is a popular Ethernet cable that powers fast and reliable internet connections. Whether you're streaming movies, gaming online, or running a small business, understanding Cat5e cable specs like speed, bandwidth, and distance limits can help you get the most out of your network. This trusty cable supports impressive speeds, including Cat5e 2.5 Gbps and even Cat5e Gigabit performance, making it a go-to choice for many. But how fast is Cat5e, and what's the max length of Cat5e before performance drops? In this guide, we'll break down the Cat5e speed rating, bandwidth, and distance limits in simple terms, so you can decide if Cat 5e Ethernet is good for your needs. Let's dive into the world of Cat5e cable speed and explore its full potential!
What is Cat5e Cable?
The Cat 5e cable (that extra "e" makes all the difference!) is an enhanced version of the Category 5 (Cat5) cable standard, used for networking. It's a type of Ethernet cable that supports higher data transfer speeds than the original Cat5, making it suitable for Gigabit Ethernet and other modern networking needs.
From Cat5 to Cat5e: A Quick Evolution
Back in the late 1990s, network engineers realized that the original Cat5 cables just weren't cutting it anymore as internet speeds increased. The Cat5e standard was introduced in 2001 as a solution, bringing significant improvements without a major price hike. While the original Cat5 was designed for 100 Mbps networks (Fast Ethernet), Cat5e cable specs were enhanced to reliably support 1000 Mbps or 1 Gbps (Gigabit Ethernet), that's 10 times faster!
Physical Construction: What Makes Cat5e Special
If you were to slice open a Cat5e cable (though please don't try this at home!), you'd find eight copper wires arranged in four twisted pairs. This twisted design isn't just for looks, it's actually clever engineering that reduces crosstalk, which is the signal interference between wire pairs.
The Cat5e cable specifications require tighter twists and stricter manufacturing standards than the original Cat5, resulting in better performance. These cables typically come with the following features:
- Four twisted pairs of copper wire (eight wires total)
- 24-gauge wire thickness (AWG)
- UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) is most common, though STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) versions exist for environments with high electromagnetic interference
- PVC or plenum-rated jacket options
- Standard RJ45 connectors at each end.

Cat5e Max Speed: Theoretical vs. Real-World Performance
Theoretical Maximum Speed of Cat5e Cable
On paper, the maximum speed of Cat5e cable is impressive, it's certified to handle 1 Gigabit per second (1000 Mbps) data transfer rates. This Cat5e speed rating makes it suitable for most home and small business applications, from streaming 4K videos to handling video conferencing without breaking a sweat.
The Cat5e bandwidth of 100 MHz is the foundation for this speed capability. Bandwidth in networking cables refers to the range of frequencies the cable can handle. With 100 MHz of bandwidth, Cat 5e speed can theoretically support that full 1 Gbps data rate over its maximum rated distance.
How does it achieve these speeds? The secret lies in the improved manufacturing standards of Cat5e over the original Cat5:
- Enhanced insulation materials
- Stricter twist rate specifications
- Better crosstalk prevention between pairs
- Improved return loss characteristics
- More rigorous testing requirements
These improvements allow for cleaner signal transmission, which translates to faster Cat5e speeds and more reliable connections.
Real-World Cat5e Speed Performance
In the real world, the speed of Cat5 cables often falls short of the theoretical maximum, and that's perfectly normal. Several factors affect actual Cat5e throughput in practical installations:
|
Factor |
Impact on Cat5e Max Speed |
|
Cable length |
Longer runs experience more attenuation (signal loss) |
|
Installation quality |
Poor terminations can significantly reduce speed |
|
Network equipment |
Your connection is only as fast as your slowest device |
|
Environmental interference |
Electrical equipment nearby can degrade performance |
|
Cable quality |
Not all Cat5e cable is created equal |

Cat5e Maximum Length and Distance Limitations
Standard Maximum Length of Cat5e Cable
The industry-standard maximum length of Cat5e cable for a single run is 100 meters, or about 328 feet. This Cat5e distance limit is based on the cable's electrical characteristics and how signals degrade over distance.
But why does this limitation exist? The answer lies in physics, specifically, a phenomenon called signal attenuation. As electrical signals travel through copper wire, they gradually lose strength (attenuate). After 100 meters, the signal in a Cat5e cable typically becomes too weak for reliable data transmission at gigabit speeds.
This attenuation happens because:
- Electrical resistance in the copper wire converts signal energy to heat
- Capacitance between wires causes signal dispersion
- External interference accumulates over distance
The 100-meter Cat5e distance standard includes all cables in a single run, including patch cables at either end. So if you have a 3-foot patch cable connecting to your router and another 3-foot cable connecting to your computer, you have 94 meters left for the in-wall or ceiling cable.
Extended Cat5e Distance Scenarios
Want to know how your Cat5e speed limit changes with distance? Here's a breakdown of performance expectations at various distances:
|
Distance |
Expected Cat5e Performance |
|
50 feet (15m) |
Full 1 Gbps with minimal signal loss |
|
100 feet (30m) |
1 Gbps with negligible degradation |
|
150 feet (45m) |
1 Gbps is still achievable with quality cable |
|
300 feet (91m) |
Approaching the limit, gigabit speeds are still possible, but you may see occasional issues |
|
500 feet (152m) |
Exceeds standard Cat5e maximum length; requires signal boosting |
When running Cat5e cable near its distance limit, consider these special considerations:
- Use higher quality cable with pure copper conductors (not copper-clad aluminium)
- Minimize the number of junctions and punch-downs
- Keep the cable away from sources of interference. For more tips, read our top tips for protecting your Ethernet cables.
- Consider using shielded Cat5e in electrically noisy environments
Beyond Gigabit: Can Cat5e Support 2.5 Gbps?
Something exciting happened in the networking world in 2016: the development of new standards that squeeze more performance out of existing cables. The NBASE-T Alliance (now part of the Ethernet Alliance) and IEEE 802.3bz standard introduced two new speed tiers: 2.5GBASE-T and 5GBASE-T.
These standards were specifically designed to bridge the gap between 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps networks, offering a pathway to higher speeds without requiring a complete cable infrastructure overhaul. The clever engineering behind these standards uses more advanced signal processing and encoding techniques to achieve higher data rates over the same physical medium.
For businesses and tech enthusiasts wondering about upgrading network speeds, these standards offered a welcome middle ground between staying at 1 Gbps or making the expensive jump to 10 Gbps infrastructure.
Can Cat5e Handle 2.5 Gbps Ethernet?
Here's the good news for Cat5e owners: Yes, in many cases, Cat5e 2.5 Gbps speeds are achievable! This is one of the most surprising capabilities of this venerable cable standard.
According to the IEEE 802.3bz specification, Cat5e cable can indeed support 2.5 Gbps up to 100 meters under ideal conditions. However, there are some important caveats to this Cat5e max speed claim:
- The cable must be of good quality and properly installed
- Both ends of the connection need 2.5GBASE-T compatible equipment (switches, NICs)
- The environment should have minimal electromagnetic interference
- Actual performance may vary based on the specific cable's characteristics
Is Cat5e Still Good in 2026?
As we navigate through 2026, is Cat5e still a viable option for network infrastructure? The answer depends largely on your specific needs, but for many applications, Cat 5e Ethernet remains entirely sufficient.
Current networking demands typically involve:
- Internet connections (usually 50 Mbps to 1 Gbps for residential)
- Video streaming (4K streaming requires about 25 Mbps)
- Video conferencing (5-10 Mbps for high-quality)
- Gaming (15-25 Mbps for most online games)
- Smart home device connectivity (minimal bandwidth requirements)

When to Upgrade from Cat5e
While Cat5e remains viable, there are situations where upgrading to a higher category cable makes sense. Learn more about the differences in our guide on Cat5e vs. Cat6 vs. Cat6a Ethernet cables. Clear indicators that Cat5e speed may no longer be sufficient include:
- Your internet service exceeds 1 Gbps
- You regularly transfer very large files between local computers
- You're experiencing network bottlenecks despite having good equipment
- You run specialized applications requiring more than gigabit speeds
- You're planning a new installation with a 10+ year outlook
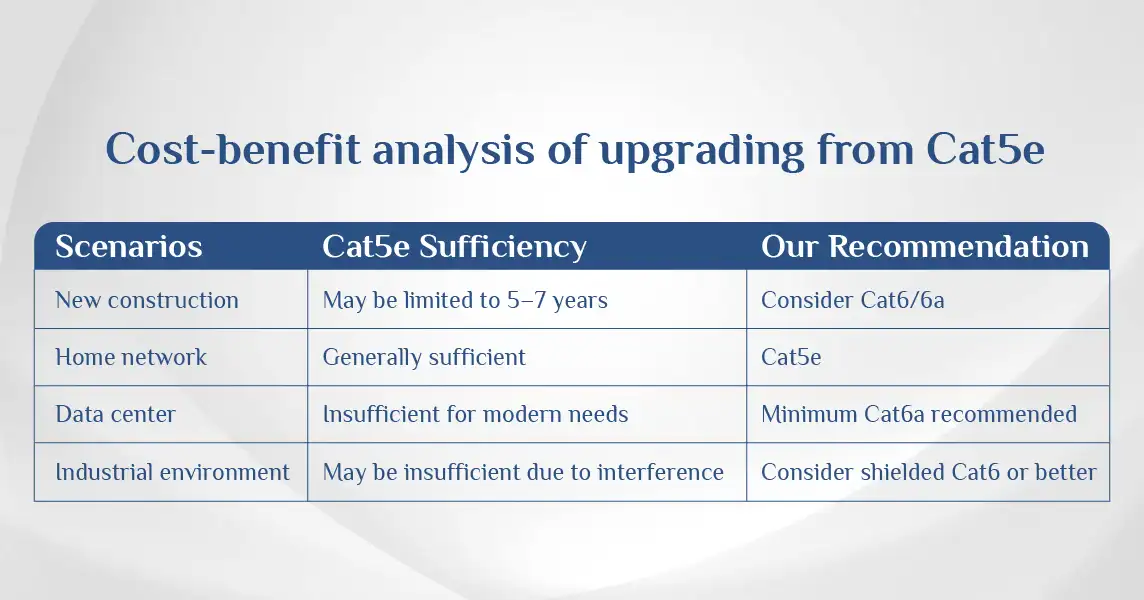
The cost-benefit analysis of upgrading from Cat5e varies by situation:
|
Scenario |
Cat5e Sufficiency |
Recommendation |
|
New construction |
May be limited to 5-7 years |
Consider Cat6/6a for future-proofing |
|
Office renovation |
Usually adequate for 3-5 years |
Balance budget vs. future needs |
|
Home network |
Generally sufficient for most users |
Cat5e still viable for most homes |
|
Data center |
Insufficient for modern needs |
Minimum Cat6a recommended |
|
Industrial environment |
May be insufficient due to interference |
Consider shielded Cat6 or better |
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of Cat5e max speed, we've seen that this versatile networking cable continues to hold its own in 2025. With a standard maximum speed of Cat5e cable at 1 Gbps and the surprising ability to support 2.5 Gbps in many scenarios, Cat 5e Ethernet remains a practical choice for many applications.
We've learned that the Cat5e distance limit of 100 meters provides ample reach for most installations, and that proper installation techniques are crucial for achieving the full cat5e speed rating. We've also examined how Cat5e bandwidth of 100 MHz translates to practical performance in real-world settings.
Whether you're setting up a new network or choosing the right Ethernet cable, maintaining an existing one, understanding the capabilities and limitations of Cat5e speed helps you make informed decisions that balance performance, cost, and future-proofing.
If you have made mind about Cat5e but still have questions, don’t hesitate to reach out at [email protected]
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the maximum speed of Cat5e cable?
The standard Cat5e max speed is 1 Gbps (1000 Mbps) at distances up to 100 meters. With newer equipment supporting the 2.5GBASE-T standard, quality Cat5e cable can potentially support 2.5 Gbps speeds over shorter distances.
How far can Cat5e cable run at maximum speed?
The Cat5e distance limit for maintaining its full 1 Gbps speed is 100 meters (328 feet). Beyond this maximum length of Cat5e, signal degradation typically prevents reliable gigabit performance without using repeaters or other signal-boosting equipment.
Can Cat5e handle gigabit speeds?
Yes, Cat5e was specifically designed to handle gigabit (1000 Mbps) speeds. Unlike the original Cat5, Cat 5e gigabit performance is guaranteed by the specification, provided the cable and installation meet the required standards.
Is Cat5e fast enough for streaming 4K video?
Absolutely! 4K video streaming typically requires 15-25 Mbps of bandwidth, well within the Cat 5e speed capabilities of 1000 Mbps. Even multiple simultaneous 4K streams would use only a fraction of the available Cat5e bandwidth.