This article is the moment of truth regarding the two cable types — Cat6 Vs Cat6a, which is superior and ideal for house installation. Let’s break the ice between the two powerful and modern ethernet cables — Cat 6 Vs 6a.
We are witnessing the world's modernization and the abrupt changes in the speed of Servers. The main reason to think and adopt the right type of ethernet cable is to maintain the data stream. Go through this article to learn about the difference between Cat 6 vs Cat 6a cable attributes, and the applications that are associated with both cables. To understand the Cat6 and Cat6a difference let's split the two cables for easy understanding.
What Is Cat6?
When you search “What is Cat6” it means you need to understand the performance of the cable, but in this guide, Smartech Cables will make you understand why these look-alike cables are entirely different.
The next advanced cable after the successful experiment of Cat5e (Enhanced Category 5 Cable) the Cat6 cable was manufactured with top-rated qualities and characteristics. Physically both cables Cat6 and Cat6a are the same but here are the specs of Cat6 Ethernet Cable.
To be precise, the Cat6 cable's main features are the tight twisted pairs that have 5-6 twists per inch to reduce the AXT (Alien Crosstalk), and NEXT (Near-End Crosstalk). Gigabit speed, 1000 Mbps over 100 meters and 50 meters the cable delivers 10 Gbps exceptional speed to provide you the best networking experience while browsing or video conferencing.
Furthermore, it is always said to choose the thickest conductor to maximize the signal strength of the cable. Likewise, you will observe a 23 AWG conductor size of the cable. Moreover, the bandwidth of the cat6 cable is 550 MHz.
Inside the cable, there is a plastic cross-skeleton material known as spline that is a helpful material to separate twisted pair cables.
What Is Cat6a?
The next cable in the pipeline is the “Augmented Category 6 Cable”, the highly advanced cable in the category of ethernet cables. Cat6 and Cat6a have the same conductor size which is 23 AWG and spline beneath the conductors, the rest of the characteristics are different.
Cat6a cable has even further improvised regarding the crosstalk and signal attenuation. The twisted pair is further tightly twisted and has 6-7 twists per inch. The core conductors are insulated with an FR PVC jacket.
However, for Cat6a cable we see a constant speed of 10 Gbps over longer (328ft) and shorter (164ft) cable length. Likewise, the cable has the tested bandwidth of 750 MHz to run high-density applications. So we can count on this Cat6a cable as it is a symbol for providing the best speed and even reducing the PS-NEXT, NEXT, and AXT.
Guaranteed Best Price !
Similarities of Cat6 Vs Cat6a
These two ethernet cables are often similar — Cat6 vs Cat6a.
- Supports 10/100/1000BASE-T (Fast and Gigabit Ethernet)
- Twisted pair design tightly twisted to fight against crosstalk
- 10GBASE-T (Future Ethernet)
- Uses T568A and T568B wiring standards
- Support 8P8C design RJ45 connector for termination (Backward Compatible)
- Both have specific jackets like riser and plenum for indoor installation
- Both have shielded or unshielded variant
- The internal core is made of a Solid Copper Conductor
- Good for PoE applications
- Better audio and video streaming
How Far Can Cat6 Vs Cat6a Go?
Don’t skip length measurement while installing the Cat6 or Cat6a cable. It is a rare phenomenon that you utilize 100 meters of cable length at your home or office. But, it does not exceed the length beyond “100 Meters” This is the maximum limit that you can install the ethernet cable.
The technical reason behind this theory is that at longer distances especially UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables, the cable is susceptible to crosstalk and the only armor to restrict crosstalk is the twisted pairs. Why you should not exceed the cable length. There are the following factors that explain problems for exceeding the length.
- Signal Loss
- Reduced Speed and Performance
- Increased Errors and Data Corruption
- Higher Risk of Connection Issues
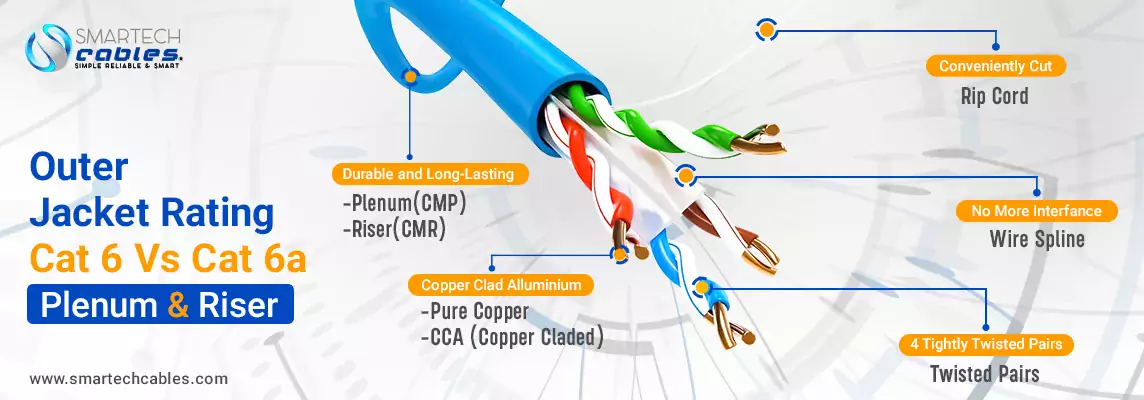
Outer Jacket Rating Cat 6 Vs Cat 6a
Cat 6 vs 6a cable has two outer jacket ratings — Plenum and Riser. The outer jackets of the cable idealize the right destinations of the cable to use for networking purposes. But you might be thinking about the similarities of the Plenum Vs Riser Jackets.
It's not easy to identify the cable jacket unless you read the printed text on Cat 6 Vs Cat 6a. First, to identify Plenum and Riser jackets manufacturers use different acronyms for Riser it is CMR whereas, for Plenum it is CMP, PLM, PL, etc. These are the simple short forms to identify the plenum or riser jackets.
What Is Plenum? Why is it so expensive? These questions might intrigue you about plenum cables. There are also various myths regarding the outer jackets. So, Plenum (CMP) is an indoor jacket of the cable which is made up of FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Polymers) — a highly fire-resistant material. The internal insulation of the cable is also made up of an FR-PVC jacket which indicates that the cable can bear temperature resistance if caused by abnormal electrical fluctuations. There are some features that plenum jacket bears
- FEP rated material
- Indoor jacket
- Thicker than riser
- UV-resistant
- Can hold harsh temperatures
- Suitable for Horizontal Shafts
- Non-toxic smoke emission (LSZH)
On the other hand, the Cat6 Vs Cat6a cable also has an Indoor Riser Jacket, a cost-effective solution for your cabling. It has the same properties as Fire-resistant and the chemical composition of the riser is PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables with riser jackets can only be used for indoor installations. The key features of Riser jackets are as follows.
- PVC rated jacket
- Indoor installation needs
- Thinner jacket than Plenum
- Less toxic smoke emission (Lack LSZH properties)
- Suitable installation in Vertical Shafts
- Protect inside conductors from damage
Pro Tip: Cat6a Vs Cat6 cables both come with Plenum (CMP) and Riser (CMR). The Cat6 or Cat6a cable is in both UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) and STP (Shielded Twisted Pair). The plenum or riser does not depict that the cable is shielded.
Shielded Vs Unshielded Cat6 or Cat6a
Should I say Best Cat6a Ethernet Cable or Best Cat6 Ethernet Cable? Well, the need and the want may vary according to the user and the server speed capacity. But there are matured and highly sophisticated types of ethernet cables — Cat6 or Cat6a.
The shielded cables (F/UTP) Foil/Unshielded Twisted Pair. Not common LAN cable for your use but these Network Cables are specially designed for some particular reasons. The UTP cable provides ease in installation, speed, performance, and better transmission speed. Whereas, the STP cables are the toughest to withstand under high EMI and RFI environments.
Inside the shielded cables (Cat 6 vs 6a) there is an additional insulation layer of Foil (F) and Braided Mess (S) within the cable. There is also a drain wire and PE tape to protect the cable. Having such a rigid structure the cable becomes bulkier and heavier and they have less bending radius for installation over sharp ends of the buildings. There are some advantages of the Shielded Cat6 Vs Cat6a Cables.
- Longer runs signal transmission
- Improved crosstalk
- Can be installed in complex wiring structures
- No signal fluctuations
- Reliability and performance
- Maximum lifespan
- Best for large data centers and network closets
Wiring Structure of Cat 6 vs Cat 6A
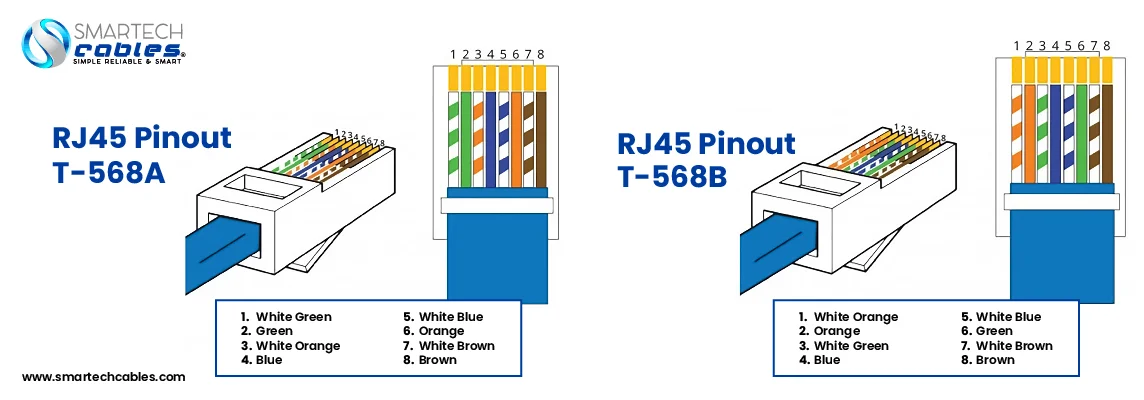
Are you aware of the twisted pair conductors of the Cat6 vs Cat6a? The core part of the cable to transfer signals. The 4 twisted pair conductors have color codes of Green/White-Green, Blue/White-Blue, Orange/White-Orange, and Brown/White-Brown respectively. These color-coded wires are then arranged accordingly with the two wiring standards to terminate the ethernet cables — T568A and T568B.
For terminating the LAN cable you need an 8P8C design RJ45 Connector. The RJ45 connector is a transparent design with 8 Positions and 8 Contacts to make viable connections after the termination process. There are two wiring standards color codes or you can say color sequence that you should follow to make a smooth transmission. For T568A and T568B following are the color codes
| T568A | T568B |
| White-Green | White-Orange |
| Green | Orange |
| White-Orange | White-Green |
| Blue | Blue |
| White-Blue | White-Blue |
| Orange | Green |
| White-Brown | White-Brown |
| Brown | Brown |
These two wiring standards are commonly used when there is a need to make a feasible connection between devices and to use Network Cables to maintain the data stream. However, the termination process is quite a simple DIY method but there are a few important things that you must be aware of.
- Do not stretch the cables beyond 110 N or 25 lbs
- A kink in the cable is always bad against the performance of the cable
- Make sure to use the same wiring standards on both ends of the cable
- Once Cat6 or Cat6a is terminated test the cable for the same wiring standards
- After inserting the conductors into the RJ45 connector make sure that they are not loose
- During cutting the cable jacket avoid cutting or damaging the cable conductor
Important Tips: For smooth networking choose the single wiring standard between T568A or T568B for bulk installation to ease the termination process for the network installer.
How Fast Is Cat 6 vs 6a?
As discussed earlier, there is a major difference between Cat6 and Cat6a but here is a technical aspect that is not ignorable — Server speed. If you adopt Cat6 it will deliver 1/10 GbE (Gigabit Ethernet) speed over 100 and 50 meters. But Cat6a cable has a constant speed over longer and shorter distances — 10 Gbps. so it implies that cat6a is faster, no matter whether the cable length is minimal or maximum.
The choice of Cat6 Vs Cat6a is a user choice. It’s better to check the speed of your server, whether it is in MBs or GBs so that you can make the best choice for the ethernet cable. The Cat6 or Cat6a cables are the right need for residential, commercial, and industrial setups to run Fast Ethernet Applications.
Final Words
Cat6 Vs Cat6a Cables — the giant in ethernet cables that are not suitable for slower or older network equipment. The demand is seamlessly increasing for fast LAN cables. For Fast Networking, you can go with the cost-effective Cat6 LAN cable or the Best Cat6a Ethernet Cable.
Before buying Ethernet Cables — Make sure to check the length, location, category, speed requirements, and the related factors to invest in the right type of cable. The war between Cat6 Vs Cat6a never ends as both are comparable supporting the gigabit network.