Have you ever wondered why your Ethernet cable comes in colours like blue, yellow, or orange? Or why do the wires inside follow a specific Ethernet cable color code? Whether setting up a home Wi-Fi network or managing a business LAN, understanding network cable color order can save you time and headaches.
Ethernet cables provide an internet connection and connect devices like computers, routers, and switches. Their color-coded wires follow standards like TIA/EIA-568 to ensure reliable connections. Each color of the Ethernet cables has a purpose; blue Ethernet cables are used for standard setups, and yellow network cables for Power over Ethernet (PoE). So if you know the Ethernet wire colors and patch cable color code, you can wire cables correctly, troubleshoot issues, and keep your network organized.
In this guide, we'll explain the Ethernet cable color order and UTP cable colour coding and answer questions like "Is a LAN and Ethernet cable the same?” Get ready to master your network with simple, expert tips!
What Are Ethernet Cables and How Do They Work?
You might wonder how we are interconnected in this world and what makes the internet connection possible. Well, most of the internet runs through roughly 500 undersea cables that connect the world, totalling about 900,000 miles. Ethernet cables are the backbone of these wired networks, connecting your devices to routers, modems, and each other.
But wait, what's the difference between an Ethernet cable and a LAN cable? Actually, nothing! They're two names for the same thing. When someone talks about LAN cables or Ethernet cables, they're referring to the same physical connection. These network cables come in several types:
- UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair): The most common type in homes and offices
- STP (Shielded Twisted Pair): Used in environments with electrical interference
- Patch cables: Short cables for quick connections
- Crossover cables: Special cables for connecting similar devices directly
See Table below to understand the details about these cable types and their features, and applications
Living in 2025, we are covered with the internet and smart technologies. And we need a cable to plug the computer into a router or connect a smart TV to the internet- that is an Ethernet cable. But have you ever looked inside one? That's where the real magic and color coding happens!
Types of Ethernet Cables and Their Uses
|
Cable Type |
Main Features |
Best Used For |
Typical Maximum Length |
|
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) |
No metal shielding, economical |
Home networks, offices with low interference |
100 meters |
|
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) |
Foil or mesh shielding around wires |
Industrial settings, areas with electrical equipment |
100 meters |
|
Patch Cable |
Factory-terminated, usually straight-through |
Quick connections between devices |
5-25 feet typically |
|
Crossover Cable |
Special wiring that swaps TX/RX pairs |
Direct computer-to-computer connections |
100 meters |
|
Plenum-Rated Cable |
Fire-resistant jacket |
In-wall or ceiling installation |
100 meters |
|
Outdoor Cable |
UV and water resistant |
Running between buildings |
100 meters |
Understanding Internal Ethernet Wire Colors
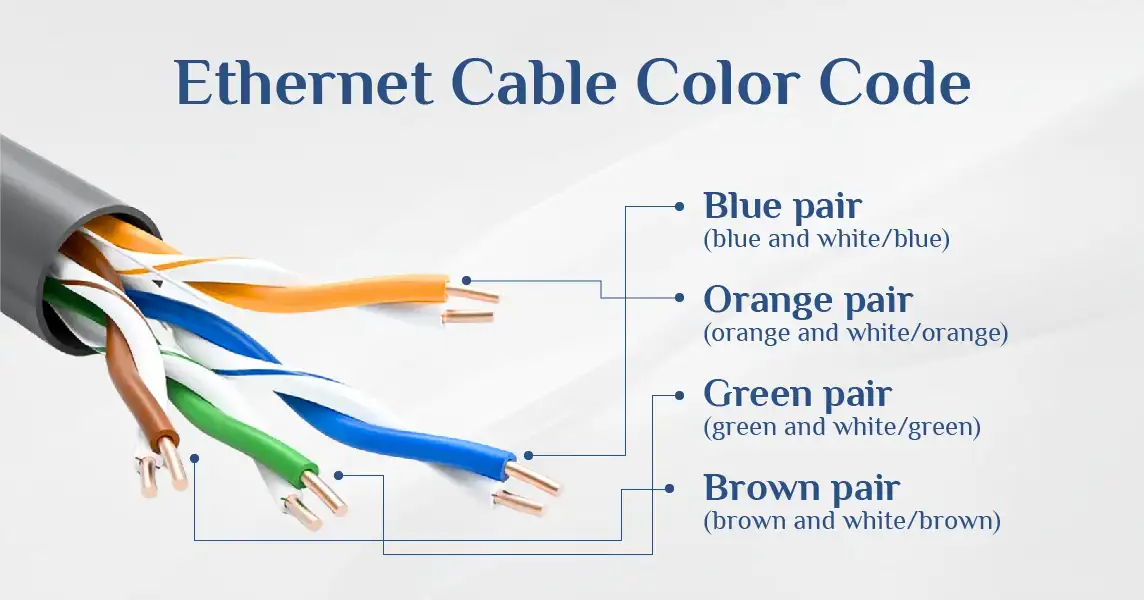
You should by now know about Ethernet cables, their types, categories, and colours. But do you know what's inside this cable? An Ethernet cable has eight tiny, colorful wires twisted into four pairs. But these Ethernet wire colors aren't random; they follow specific patterns called color codes. These standards ensure that the network cable colour order remains consistent no matter who makes the cable or where you buy it.
These Ethernet cables have a solid-colored wire and a white wire with a matching colored stripe. For example, a solid blue wire is paired with a white-and-blue striped wire. This consistent Ethernet cabling color code system helps technicians install and repair networks worldwide without confusion. See the diagram below;
T568A vs. T568B: The Two Main Wiring Standards
When it comes to Ethernet cable color codes, two main standards rule the networking world: T568A and T568B. These standards, established by the Telecommunications Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), define the exact Ethernet color order for the eight wires inside your cables.
T568A Color Code:
- White/Green
- Green
- White/Orange
- Blue
- White/Blue
- Orange
- White/Brown
- Brown
T568B Color Code:
- White/Orange
- Orange
- White/Green
- Blue
- White/Blue
- Green
- White/Brown
- Brown
The main difference? T568B swaps the positions of the green and orange pairs. While both standards work perfectly fine, T568B has become more popular in the United States, especially for new installations. T568A maintains better compatibility with older telephone wiring systems.
T568A vs T568B Wiring Standards Comparison
|
Pin Number |
T568A Wire Color |
T568B Wire Color |
Wire Function |
|
1 |
White/Green |
White/Orange |
Transmit+ |
|
2 |
Green |
Orange |
Transmit- |
|
3 |
White/Orange |
White/Green |
Receive+ |
|
4 |
Blue |
Blue |
Unused/PoE |
|
5 |
White/Blue |
White/Blue |
Unused/PoE |
|
6 |
Orange |
Green |
Receive- |
|
7 |
White/Brown |
White/Brown |
Unused/PoE |
|
8 |
Brown |
Brown |
Unused/PoE |

Here's a pro tip: Whatever standard you choose, stick with it throughout your entire network. Mixing these Ethernet connection wiring diagrams can lead to serious headaches!
Ethernet Cable Color Order for Different Categories
Not all Ethernet cable categories are created equal! As technology advances, newer cable categories offer faster speeds and better performance. Let's explore the network cable color code for different Ethernet cable categories:
Cat5 Color Code
The original category 5 cables follow standard color code cat5 cable patterns (either T568A or T568B). These older cables supported up to 100 Mbps and are mostly obsolete now, but you might still find them in older buildings.
Cat5e Color Code
Cat5e (the "e" stands for enhanced) uses the same colour code as Cat5 but with stricter manufacturing standards. The cable color code follows either T568A or T568B and supports speeds up to 1 Gbps. Cat5e remains one of the most common cable types in homes and small businesses. Explore Smart Tech's premium Cat5e Riser options and Plenum.
Cat6 Cable Color Code.
Cat6 Ethernet cables are the most widely used and allow the same wire color patterns. These cables have better insulation and sometimes include a plastic separator between pairs. Cat 6 cable color coding remains consistent with T568A or T568B standards while supporting up to 10 Gbps for shorter distances.
Cat6a Colour Code
The colour code for Cat6a (augmented) stays the same as that of other standards, but these cables have even more robust shielding. The Cat6a cables color code doesn't change; the physical construction improves performance up to 10 Gbps for longer distances.
Ethernet Cable Categories Comparison
|
Cable Category |
Max Speed |
Max Length for Highest Performance |
Internal Color Code |
Physical Differences |
|
Cat5 |
100 Mbps |
100 meters |
T568A/B |
Basic insulation, no separator |
|
Cat5e |
1 Gbps |
100 meters |
T568A/B |
Improved twist ratios, better crosstalk reduction |
|
Cat6 |
10 Gbps |
55 meters (10 Gbps), 100 meters (1 Gbps) |
T568A/B |
Thicker insulation sometimes includes a spline separator |
|
Cat6a |
10 Gbps |
100 meters |
T568A/B |
Heavy shielding, rigid construction, always includes a separator |
|
Cat7 |
10 Gbps |
100 meters |
T568A/B |
Individual pair shielding plus overall shield, GG45 connectors |
|
Cat8 |
40 Gbps |
30 meters |
T568A/B |
Heavy shielding, extremely strict twist requirements |
Outer Jacket Colors: What Do They Mean?
Have you ever wondered why Ethernet cables come in so many colors? Those outer jacket colors aren't just for show, they often serve specific purposes in network organization.
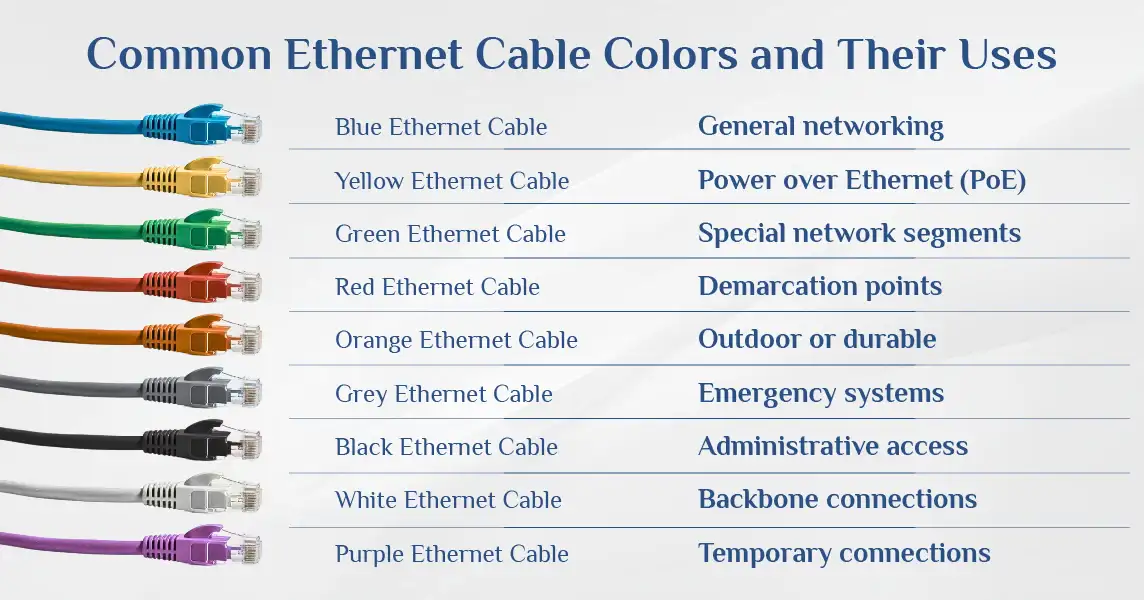
Common Ethernet Cable Colors and Their Uses
-
Blue Ethernet Cable
Blue Ethernet cables are the most common. They typically indicate standard network connections in business environments. When you see a blue Ethernet cable, it's usually a general-purpose cable connecting computers to the network.
- Yellow Network Cable
Many organizations use yellow Ethernet cords to identify Power over Ethernet (PoE) connections that deliver both data and electrical power to devices like security cameras, wireless access points, or Ethernet cables for streaming.
-
Green Ethernet Cord
The green Ethernet cord frequently identifies crossover connections or special network segments. In some organisations, green cables mark connections to servers or specific departmental networks.
-
Orange Ethernet Cable
An orange cable Ethernet connection often indicates demarcation points or connections to critical infrastructure. When you spot orange Ethernet cables like Cat5 or Cat6 augmented, they might be connecting to the building's main telecommunications room.
-
Black Ethernet Cable
Black Ethernet cables are commonly used as outdoor or weather-resistant options. Their dark color helps protect against UV degradation, making them perfect for running between buildings or in exposed areas.
-
Other Colors
Other colours, from purple to red to white, help organizations customize their network color-coding systems. For example, red might indicate emergency systems, while purple could mark special administrative connections. At Smart Tech Cables, we offer all these colors of Cat5e, Cat6 and Cat6a Bulk Ethernet cables
Common Ethernet Cable Jacket Colors and Their Typical Uses
|
Cable Color |
Common Industry Use |
Typical Application |
Special Considerations |
|
Blue |
General networking |
User workstations, standard connections |
Most common, often the default choice |
|
Yellow |
Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
Security cameras, WiFi access points, VoIP phones |
Identifies connections with power delivery |
|
Green |
Special network segments |
Server connections, crossover connections |
Often used for distinct network zones |
|
Orange |
Demarcation points |
ISP connections, building infrastructure |
Critical connections, main feeds |
|
Black |
Outdoor or durable |
Between buildings, exposed areas |
UV resistant, sometimes weatherproof |
|
Red |
Emergency systems |
Fire alarms, security, critical infrastructure |
Reserved for essential systems |
|
Purple |
Administrative access |
Management networks, console connections |
Limited access connections |
|
Gray |
Backbone connections |
Between network distribution points |
High-capacity trunk lines |
|
White |
Temporary connections |
Testing, non-permanent setups |
Easy to spot as non-standard |
Yellow vs. Blue Ethernet Cable: What's the Difference?
As you know from above the table, lists the different Ethernet cable colors and their functions and features. But the question is, "Is there a functional difference between yellow and blue Ethernet cable choices?" Not really! The cable color doesn't affect performance; a yellow Cat6 cable works exactly the same as a blue one with the same specifications. The difference lies in how organizations use colors to organize their networks.
Many IT departments use blue for general connections and yellow for special purposes like PoE or guest networks. This color-coding makes troubleshooting much faster. Imagine trying to find one specific cable in a server room with hundreds of identical black cables!
Benefits of Color-Coded Ethernet Cables
Color-coded ethernet cables might seem like a small detail, but they make a huge difference in network management:
- Faster troubleshooting: Technicians can identify cable purposes at a glance
- Reduced downtime: Studies show organizations with color-coded systems experience 25% less network downtime
- Easier maintenance: When upgrading or modifying the network, color codes prevent accidental disconnections
- Better documentation: Network diagrams can reference colors for clearer instructions
- Enhanced safety: Critical systems can be clearly marked to prevent accidental disruption
Conclusion
From understanding an Ethernet cable's colour to mastering UTP cable colour coding, we've covered everything you need to know about Ethernet cable color codes. These seemingly simple color patterns inside and outside your cables are crucial in building and maintaining reliable networks.
Whether setting up a home network or managing an enterprise system, paying attention to Ethernet wire colour code standards can save you countless hours of troubleshooting and prevent costly mistakes. The next time you look at what an Ethernet cable looks like, you'll understand the meaning behind every color!
FAQS
What is the color code for an Ethernet cable?
The ethernet cable color code follows T568B (most common): White/Orange, Orange, White/Green, Blue, White/Blue, Green, White/Brown, Brown. T568A is an alternative standard.
What color code is best for Ethernet cable?
Due to its widespread use, T568B is best for most U.S. networks. Choose T568A for older or government setups.
How do I arrange my Ethernet cable colors?
Strip the cable, arrange wires in T568B order (White/Orange, Orange, White/Green, Blue, White/Blue, Green, White/Brown, Brown), trim, and crimp into an RJ45 connector.
Does it matter what colour Ethernet cable I use?
The outer network cable color doesn't affect performance, but helps organization (e.g., blue for standard, yellow for PoE). Internal Ethernet wire colors must follow T568A or T568B.
What color Ethernet cable is the fastest?
Speed depends on cable category (e.g., Cat6, Cat6a), not color. Any color Ethernet cable can be fast if it's the right category.
Can I use a yellow Ethernet cable for internet?
Yes, a yellow network cable works for the Internet and is often used for Power over Ethernet (PoE). Performance depends on the cable’s category, not its color.